Recently, researchers led by Prof. Tao Zhang and Changzhi Li from the Catalysis and New Materials Research Center (Group 1500), in collaboration with Prof. Yingwei Li at South China University of Technology, developed a robust atomically dispersed Cu/Ni-SA@HNC catalyst for lignin valorization. By employing a unique "preferential cleavage of Cα-Cβ bonds in β-O-4 linkages" pathway, they achieved ultra-selective hydrogenolysis of lignin and model compounds to toluene, offering a novel strategy for activating lignin's recalcitrant C-C bonds and enabling selective lignin depolymerization.
Lignin refining still faces significant challenges of low selectivity and activation of stubborn C-C bonds. In this study, the team prepared an atomically dispersed Cu/Ni-SA@HNC catalyst with exceptional stability, which selectively cleaves Cα-Cβ bonds in β-O-4 linkages rather than C-O bonds. The catalyst delivered a remarkable toluene yield of 75.7% from β-O-4 model compounds and 33.7±1.6 wt% from poplar lignin (nine parallel experiments, Figure 1). Through comprehensive catalyst characterization, control experiments, and theoretical calculations, the intrinsic mechanism behind the catalyst's unique selectivity for Cα-Cβ bond cleavage over C-O bond scission was disclosed. Moreover, the catalyst exhibited high stability in recycling tests, and its potential for industrial-scale application was demonstrated by a high space-time yield (33.7 g gcat⁻¹ h⁻¹) in a continuous-flow reaction using β-O-4 model compounds.
This work addresses two major challenges in lignin valorization—selective depolymerization of its complex structure and C-C bond activation—by employing a non-noble bimetallic single-atom catalyst. It not only highlights the promise of atomically dispersed catalysts in biorefinery applications but also provides a petroleum-independent route for producing bulk aromatic chemicals.
The findings were recently published in Nature Communications under the title "Catalytic refining lignin into toluene over atomically dispersed Cu/Ni dual sites." This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the NSFC Basic Science Center for "Single-Atom Catalysis." (Text/Images: Qian Qian, Changzhi Li)
Publication Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-63286-5
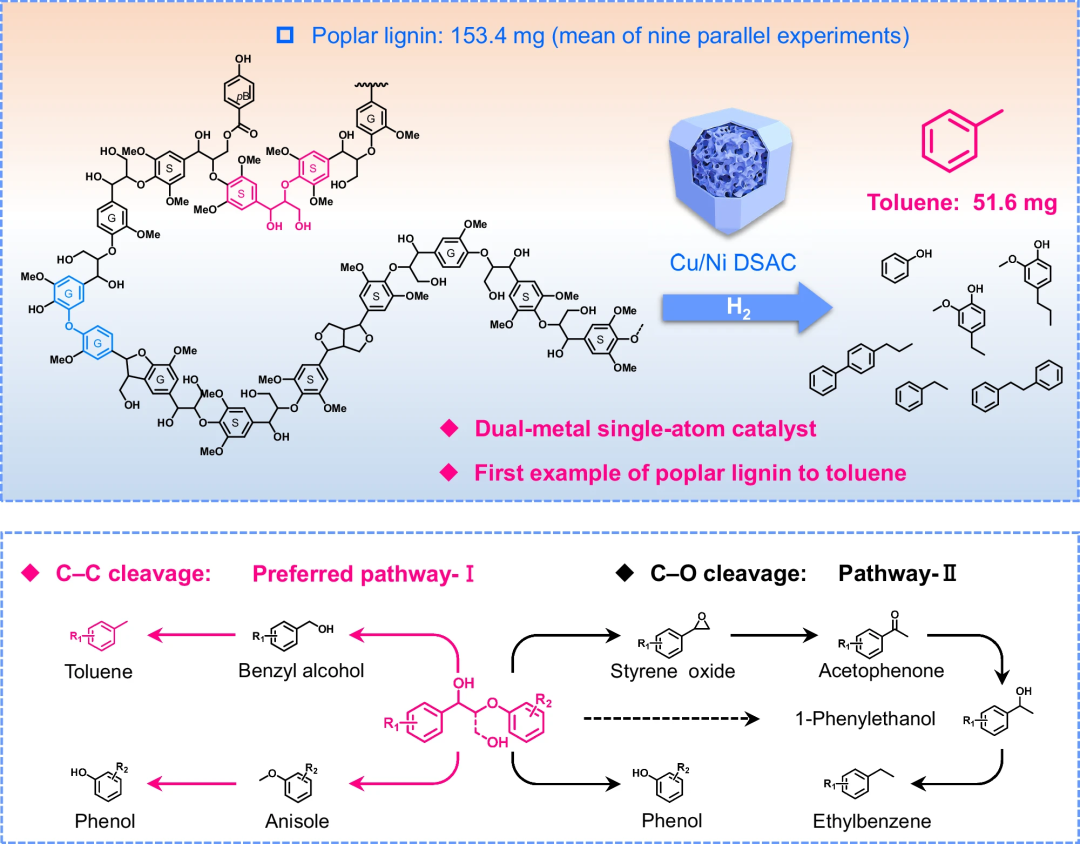
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the catalytic refining of poplar lignin and β-O-4 model compounds into toluene over Cu/Ni-SA@HNC catalyst.